- An Introduction to Self-Driving Car
- Machine Learning Algorithms and Techniques in Self-Driving Cars
- Localization for Self-Driving Cars
- Perception for Self-Driving Cars
- Hardware and Software Architecture of Self-Driving Cars
- Sensor Fusion for Self-Driving Car
- Self-Driving Car Path Prediction and Routing
- Self-Driving Car Decision-Making and Control System
- Cloud Platform for Self-Driving Cars
- Dynamic Modeling of Self-Driving Car
- Safety of Self-Driving Cars
- Testing Methods for Self-Driving System
- Operating Systems of Self-Driving Cars
- Training a YOLOv8 Model for Traffic Light Detection
- Deployment of Self-Driving Cars
An Introduction to Self-Driving Car | Self Driving Cars
What is a self-driving car
A self-driving car is a wonder of modern AI technology which is capable of detecting its surroundings and functioning without any human intervention. To be considered completely autonomous, a vehicle must be able to go to a preset location without human intervention on roads that have not been adapted for its usage. A driverless automobile must know the route, understand its environment, follow traffic regulations, and make accurate decisions while interacting with other cars and people on the road in order to arrive at its destination.

Technologies behind self-driving cars
The goal of autonomous cars is to eliminate the need for a driver, allowing all passengers to enjoy the ride. For this, technology must advance to a degree of security that can be relied upon. To achieve the goal numerous hardware, software and algorithms are working behind it.
Hardware
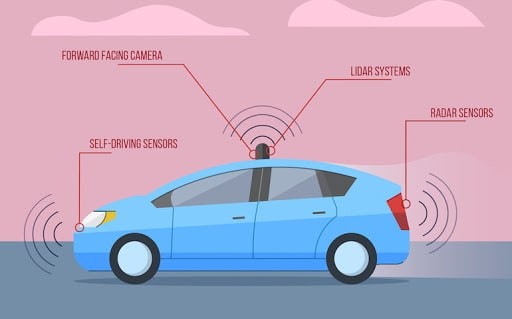
Hardware components are in charge of sensing environmental factors and relaying that information to the onboard computer. Cameras, radars, sonars, and LIDARs are now the most popular. The most commonly used sensors and hardware are given below
- Stereoscopic camera
- Infrared camera
- Radar
- Sonar
- Lidar
- Electronic Stability Control
- GNSS, GPS, speedometer, and odometer
Software
While the autonomous car's physical components allow it to execute activities such as seeing, talking and driving, the software acts as the brain, processing information from the surroundings to determine what action to take—whether to drive, stop, slow down, and so on. These tasks are given below:
- Object detection
- Object classification
- Object localization
- Prediction of movement
How to achieve autonomy
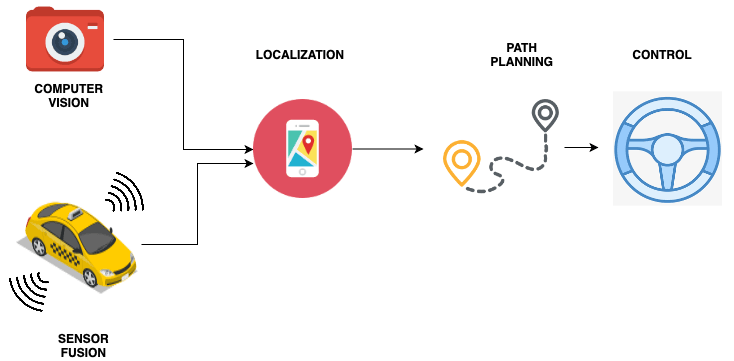
Every self-driving car uses our four key processes to achieve autonomy: perception, localization, planning, and control.
Perception
This stage allows multiple various sensors (camera, LiDAR, RADAR, etc.) to work together to determine where the road is and what the condition (type, location, and speed) of each obstacle is. This is how we characterize the perception of the world in which our car operates. The perception system refers to the autonomous car's capacity to determine which sensors or V2V components provide the required information.
Localization
The idea of localization is to place the vehicle within 1–3 cm of its intended location in the environment. Some cars use GNSS or GPS, while others use cameras and LiDAR data. This stage uses extremely precise maps (HD Maps) as well as sensors like GPS, camera, LiDAR, etc to figure out where the automobile is in its surroundings to the centimeter level.
Planning
A self-driving car's capacity to make specific decisions in order to attain higher-order goals is referred to as the planning system. And the self-driving car understands what to do in a certain circumstance, such as pause, move, or slow down. The Planning stage plans paths to a destination using information about the car's location and barriers. Here, The application of the law is programmed, and the algorithms determine waypoints. This is what makes decisions and directs the vehicle to a specific location.
Control
The control system is responsible for converting the planning system's goals and priorities into actions. Here, the control device informs the appropriate inputs' hardware actuator leading to the needed motions. The algorithms are created to follow the waypoints effectively, taking into consideration the route and the vehicle. This controls the vehicle's brakes, acceleration, and steering wheel. For example, an autonomous car recognizing it should slow down while approaching a red light.
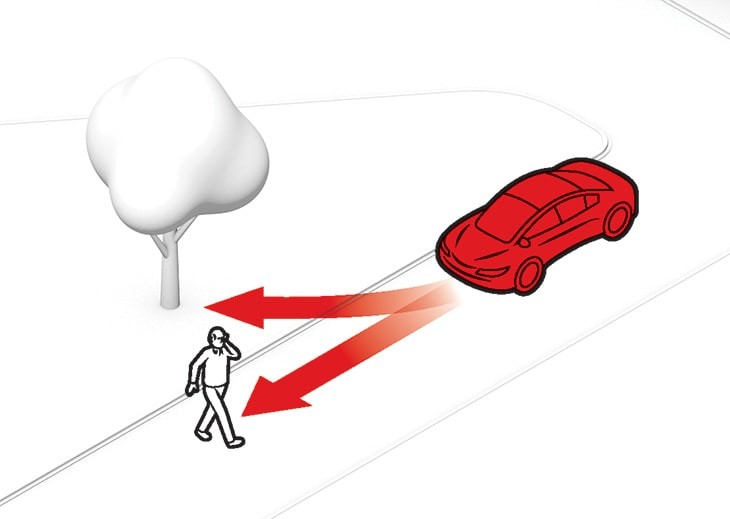
Self-driving car safety and challenges
The main challenge for self-driving cars is identifying numerous things in their route, ranging from branches and garbage to animals and humans. Tunnels that interfere with GPS, construction projects that cause lane changes, and difficult judgments, such as where to stop to let emergency vehicles pass, are all obstacles on the road. The challenges range from technological to environmental and philosophical in nature. Here are only a few of the challenges are given,
- Weather Conditions
- Traffic Conditions and Laws
- Accident Liability
- Cybersecurity risks
- Artificial vs. Emotional Intelligence
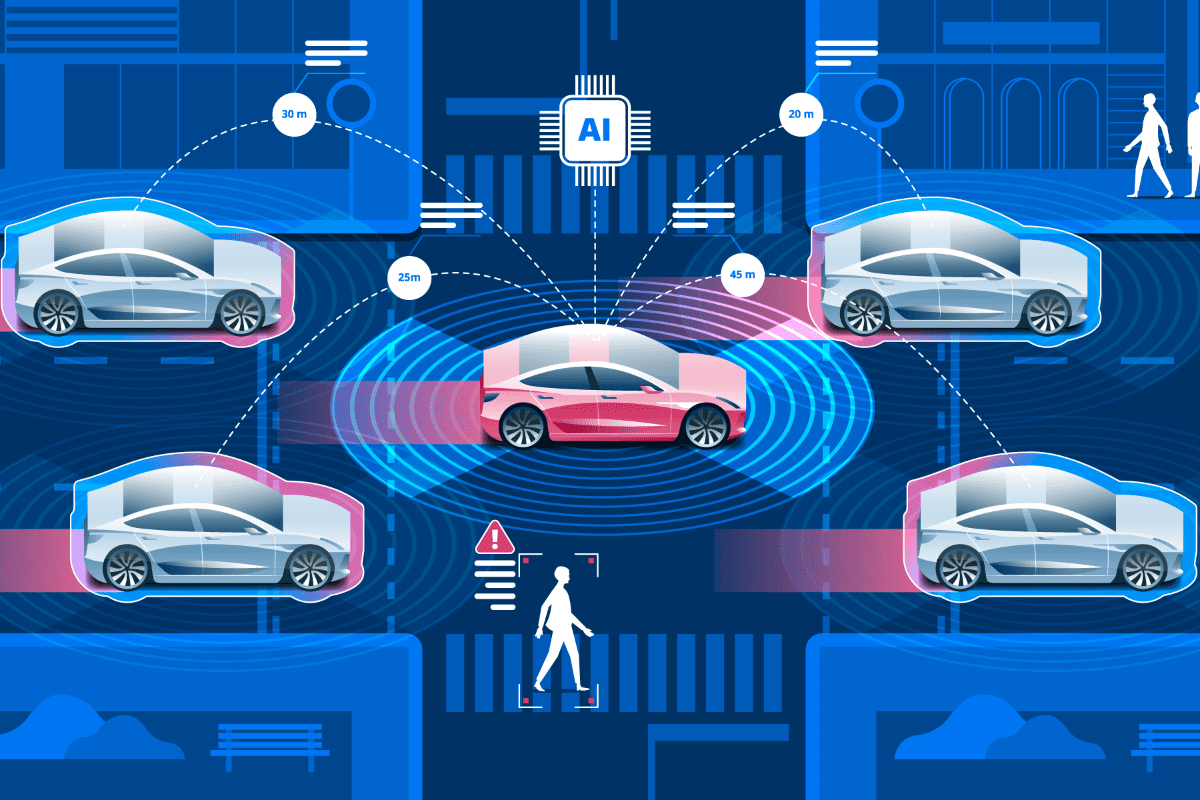
Artificial Intelligence and Connectivity
Artificial Intelligence plays an important role in self-driving cars for collecting all sensor signals, monitoring driving, generating maintenance requirement alerts, making minor device changes and updates, and learning from failure. Connectivity with other self-driving cars can allow exchanging information.
Conclusion
The rise of self-driving cars is a direct result of the collective imagination. We are witnessing an evolution based on rapid technological progress, and human mobility may never be the same again, sooner or later. We have no idea how many twists and turns are in store for us, but the road to our destination is certainly thrilling.
Thank you for reading the tutorial. Hope that clarifies what a self-driving automobile is. If you're further interested in this topic you can check your website for more tutorials on this topic.
If you have any suggestions or queries you can comment below. Your comments are always important to us.