- An Introduction to Self-Driving Car
- Machine Learning Algorithms and Techniques in Self-Driving Cars
- Localization for Self-Driving Cars
- Perception for Self-Driving Cars
- Hardware and Software Architecture of Self-Driving Cars
- Sensor Fusion for Self-Driving Car
- Self-Driving Car Path Prediction and Routing
- Self-Driving Car Decision-Making and Control System
- Cloud Platform for Self-Driving Cars
- Dynamic Modeling of Self-Driving Car
- Safety of Self-Driving Cars
- Testing Methods for Self-Driving System
- Operating Systems of Self-Driving Cars
- Training a YOLOv8 Model for Traffic Light Detection
- Deployment of Self-Driving Cars
Perception for Self-Driving Cars | Self Driving Cars
Perception refers to an autonomous system's ability to absorb information and extract valuable knowledge from its environment. The process of obtaining contextual knowledge of the environment, such as finding obstacles, detecting road signs and markings, and categorizing data according to its semantic meaning, is known as environmental perception. For self-driving cars, it is the most difficult and complex task to sense the environment and make the decision accordingly. For receiving and processing data, self-driving cars use various sensors and algorithms. knowing the environment and perception is the most important task for a self-driving car to drive the car autonomously. Without knowing the environment the car will not be able to make proper decisions. In this article, we are going to discuss environmental circumstances and perceptions of self-driving cars.
1. Environmental Perception
Environment perception is a critical function for autonomous cars since it supplies the vehicle with critical information about the driving environment, such as the free drivable regions and the positions, velocities, and even forecasts of future states of surrounding impediments. The environment perception job can be handled with LIDARs, cameras, or a combination of these two types of devices, depending on the sensors used. One of the difficult issues in environmental perception is that a vehicle is usually a part of the whole system being perceived and certainly moves over time within the environment. The vehicle should also sense its whole surrounding and provide the robust detection of stationary and movable objects to utilize them separately in subsequent algorithms.
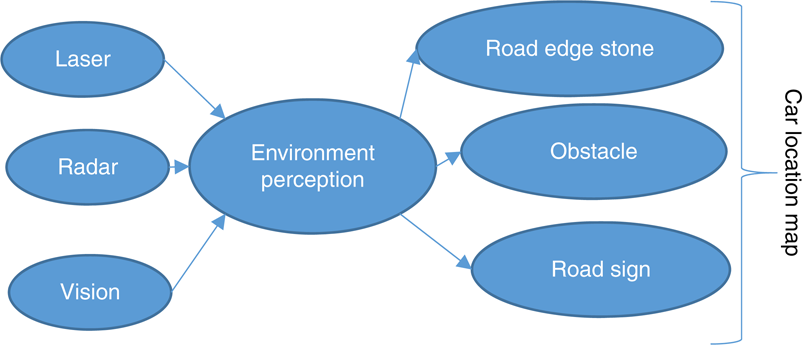
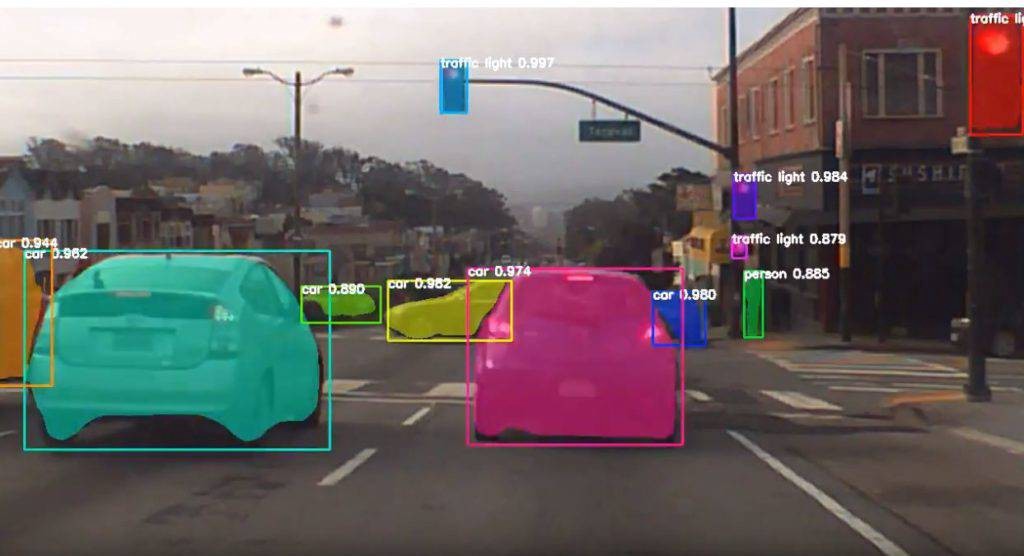
2. Object Detection
Vehicles, persons, animals, and other objects must be detected with their precise distances from the vehicle. The behavior of nearby objects must be understood or predicted to regulate the vehicle's movement. Sensory input equipment such as cameras, radar, and lasers are required for an autonomous vehicle to sense the environment around it and create a digital map.
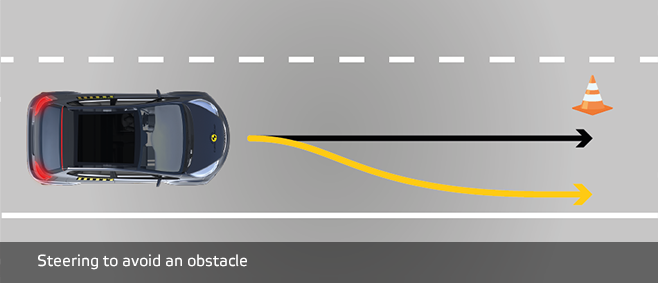
3. Obstacle Avoidance
Obstacle avoidance is a crucial part of self-driving car navigation. A good path must avoid both static and moving obstacles of arbitrary shape as the vehicle moves from any arbitrary start locations to any arbitrary goal positions in the environment. The object detection module provides input to the obstacle avoidance module. It finds its path around the barrier using the A* algorithm. It has a 100-meter look-ahead distance.
4. Segmentation
Segmentation is a method of scene comprehension in which each pixel of an image is classified. In autonomous cars, semantic segmentation is used to find frontal items such as roadways, dividers, automobiles, pavements, and so on. It's an important component of the vehicle's navigation system. The relevance of each class in a self-driving system cannot be taken into account by the cross-entropy loss. For example, while making driving judgments, pedestrians in the image should be far more relevant than surrounding buildings, thus segmentation results should be as precise as feasible.

5. Mapping
As driving shifts from humans to robots, digital maps' purpose and breadth expand beyond navigation. GPS systems can't keep up with self-driving cars because they don't give data that is dynamic and accurate enough. To extend their vision and offer a complete inventory of road characteristics and objects on the side of the road, autonomous driving software requires self-healing mapping autonomous vehicles systems specifically developed for self-driving cars. The integration of this automobile big data shows the car's exact location concerning all landmarks, providing full, real-time information on road limits, traffic signals, and lane placement. As a consequence, high-definition maps provide an accurate depiction of the route with laser-sharp precision, setting a new benchmark for autonomous vehicle in-car navigation systems.
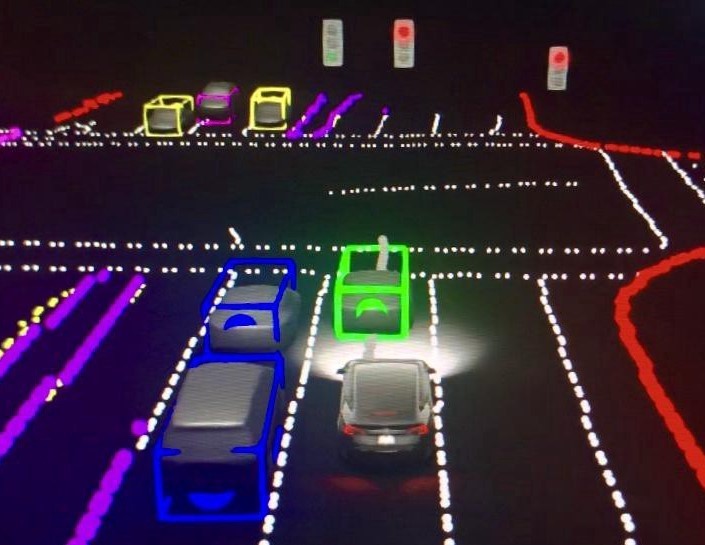

6. Multiview perception
Multiview perception gives the ability to a self-driving car to see and perform better. Multiview systems, for example, may recognize an unknown item in the distance, capture the precise distance from the vehicle, and come to a complete stop in real-time. These systems are able to better and more reliably detect things by capturing high-resolution, accurate, and robust data from the surrounding scenes. Furthermore, multiview perception systems may record depth, allowing them to distinguish between a moose and a photograph of a moose, reducing the number of collisions and vehicle damage.
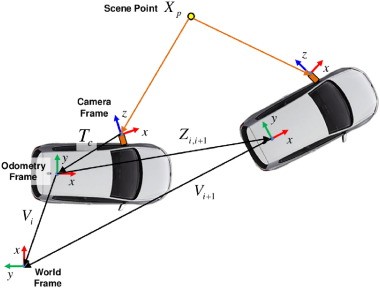
Conclusion
Localization is an essential topic for self-driving cars. We can drive autonomously if we can locate our car extremely precisely. This field is continuously changing; sensors are becoming more precise, and algorithms are becoming more efficient. We can now create algorithms for designing trajectories and making decisions for our self-driving automobiles.
Thank you for taking the time to read this article. I hope that gave you a quick overview of self-driving car perception analysis approaches. Feel free to leave a comment below if you have any questions or suggestions about the post. Your feedback is always valuable to us.