- An Introduction to Machine Learning | The Complete Guide
- Data Preprocessing for Machine Learning | Apply All the Steps in Python
- Regression
- Learn Simple Linear Regression in the Hard Way(with Python Code)
- Multiple Linear Regression in Python (The Ultimate Guide)
- Polynomial Regression in Two Minutes (with Python Code)
- Support Vector Regression Made Easy(with Python Code)
- Decision Tree Regression Made Easy (with Python Code)
- Random Forest Regression in 4 Steps(with Python Code)
- 4 Best Metrics for Evaluating Regression Model Performance
- Classification
- A Beginners Guide to Logistic Regression(with Example Python Code)
- K-Nearest Neighbor in 4 Steps(Code with Python & R)
- Support Vector Machine(SVM) Made Easy with Python
- Kernel SVM for Dummies(with Python Code)
- Naive Bayes Classification Just in 3 Steps(with Python Code)
- Decision Tree Classification for Dummies(with Python Code)
- Random forest Classification
- Evaluating Classification Model performance
- A Simple Explanation of K-means Clustering in Python
- Hierarchical Clustering
- Association Rule Learning | Apriori
- Eclat Intuition
- Reinforcement Learning in Machine Learning
- Upper Confidence Bound (UCB) Algorithm: Solving the Multi-Armed Bandit Problem
- Thompson Sampling Intuition
- Artificial Neural Networks
- Natural Language Processing
- Deep Learning
- Principal Component Analysis
- Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA)
- Kernel PCA
- Model Selection & Boosting
- K-fold Cross Validation in Python | Master this State of the Art Model Evaluation Technique
- XGBoost
- Convolution Neural Network
- Dimensionality Reduction
A Beginners Guide to Logistic Regression(with Example Python Code) | Machine Learning

In this article, we will go through the concept of logistic regression, a simple classification algorithm. Then we will implement the algorithm in Python.
Logistic Regression Intuition:
Logistic Regression is the appropriate regression analysis to solve binary classification problems( problems with two class values yes/no or 0/1). This algorithm analyzes the relationship between a dependent and independent variable and estimates the probability of an event to occur. Like other regression models, it is also a predictive model. But there is a slight difference. While other regression models provide continuous output, Logistic Regression is used to model the probability of a certain class or event existing such as pass/fail, win/lose, alive/dead or healthy/sick.
A good example can be finding the probability of getting cancer(yes/no) by a person for smoking for some years based on the dataset of people containing their smoking period, age, and the condition(having cancer or not).
How this Algorithm Works?
If you remember the regression, you can understand that in regression, we use a function to predict the probability of an event to occur. In logistic regression, the idea is the same but with that function, we combine another function named sigmoid or logistic function to find the probability. You can better understand from the following illustration-
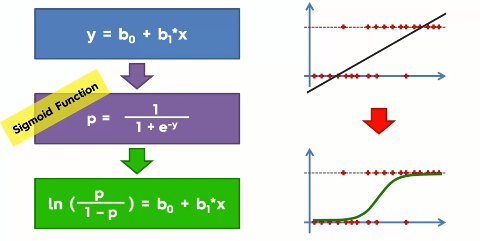
Top of the illustration you can see the original regression equation(at left) and the resulting regression line(at the right of the top). And when we combine it with the sigmoid function we get the logistic equation(in the green box at the bottom). And the resulting slope is shown at the bottom right.
Well, with this logistic function you will get the probability of an event to occur like the probability of buying a car by a person of a certain age.
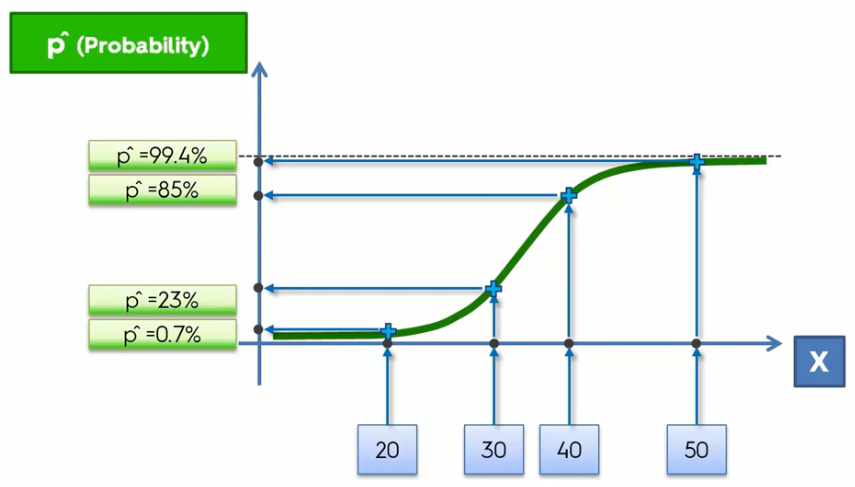
Here, you can see that people of a lower age(between 20 to 30) are less likely to buy a car(between 0.7% to 23%) whereas people of higher ages have more probability.
But wait! We are doing classification and we want the probability of people buying a car or not(yes/no values) but here we get a continuous probability. So what would we do is that we will take a threshold point(like 50% or 0.5) in the graph and based on that line we will calculate the probability.
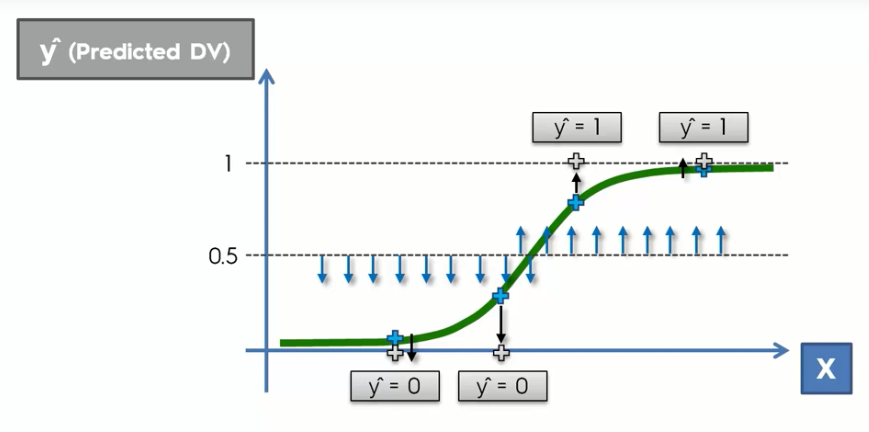
Here you can see we take a threshold point(50% or 0.5) where anything under that probability classified as a 0 or no value and above that line the probability is classified as 1 or yes.
This way we can use a regression function to solve classification problems.
Logistic Regression in Python :
Now we will implement this algorithm in Python. Here we take a dataset containing the Age, Salary, and Action(yes/no value) of purchasing a car. Now our task is to classify a person in terms of his Age and Salary whether he/she is supposed to buy the car.
You can download the dataset from here.
First of all, we import essential libraries. You will get the code in Google Colab also.
# Importing Essential Libraries
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import pandas as pd
Now, we will import the dataset to our program.
# Importing the Dataset
dataset = pd.read_csv('Social_Network_Ads.csv')
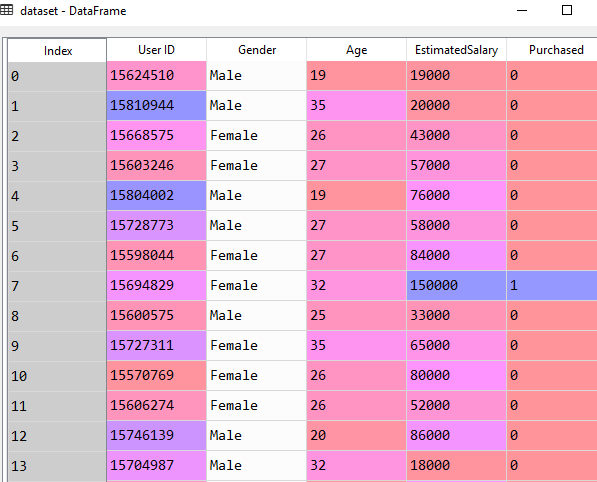
In this dataset, the Age and EstimatedSalary column are independent variables and the last column Purchased is the dependent variable. The last column contains the values 0 or 1. It means it provides the output like yes or no.
Now we take the indexes of Age and EstimatedSalary as our independent variable matrix. And take the Purchased column in the dependent variable vector.
X = dataset.iloc[:, [2, 3]].values y = dataset.iloc[:, 4].values
Now we split the dataset into a training set and a test set. For this, we take the test size=0.25%. And execute it. After execution, we get 300 training sets and 100 test sets.
# Splitting the Dataset into Training and Test Set from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 0.25, random_state = 0)
Now, we will do feature scaling. To transform the x_train matrix object to scale, we use the fit_transform method.
# Scaling the Datasets from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler sc = StandardScaler() X_train = sc.fit_transform(X_train) X_test = sc.transform(X_test)
Now, we fit a logistic regression to the training set. We use the linear model library to import the class LogisticRegression. Then we create the classifier object and call that object.
# Fitting the Datataset with Regression Class from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression classifier = LogisticRegression(random_state = 0) classifier.fit(X_train, y_train)
Note: Here we set the random_state to zero so that the result in our program and yours remain the same.
Well, we have come to the final part of the algorithm. Let's create a variable to predict the result.
# Predicting the output y_pred = classifier.predict(X_test)
Now, we will see how good our model is to predict the values. Let's evaluate our model using the confusion matrix.
# Building the Confusion Matrix from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
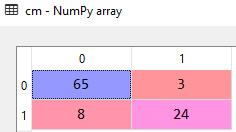
Here the output shows us that the model predicted 89 (65 + 24) correct and 11(8 + 3) incorrect values. So the accuracy of the model is 89%, pretty impressive!
Now we will visualize the result of our model.
# Visualising the Test set results
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
X_set, y_set = X_test, y_test
X1, X2 = np.meshgrid(np.arange(start = X_set[:, 0].min() - 1, stop = X_set[:, 0].max() + 1, step = 0.01),
np.arange(start = X_set[:, 1].min() - 1, stop = X_set[:, 1].max() + 1, step = 0.01))
plt.contourf(X1, X2, classifier.predict(np.array([X1.ravel(), X2.ravel()]).T).reshape(X1.shape),
alpha = 0.75, cmap = ListedColormap(('red', 'green')))
plt.xlim(X1.min(), X1.max())
plt.ylim(X2.min(), X2.max())
for i, j in enumerate(np.unique(y_set)):
plt.scatter(X_set[y_set == j, 0], X_set[y_set == j, 1],
c = ListedColormap(('red', 'green'))(i), label = j)
plt.title('Logistic Regression (Test set)')
plt.xlabel('Age')
plt.ylabel('Estimated Salary')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
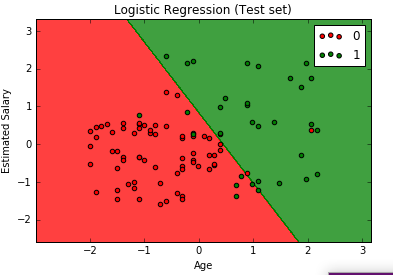
Here the graph shows us the classification of purchasing a car or not based on various Ages and EstimatedSalary.