- Getting Started with Generative Artificial Intelligence
- Mastering Image Generation Techniques with Generative Models
- Generating Art with Neural Style Transfer
- Exploring Deep Dream and Neural Style Transfer
- A Guide to 3D Object Generation with Generative Models
- Text Generation with Generative Models
- Language Generation Models for Prompt Generation
- Chatbots with Generative AI Models
- Music Generation with Generative Models
- A Beginner’s Guide to Generative Design
- Video Generation with Generative Models
- Anime Generation with Generative Models
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
- Generative modeling using Variational AutoEncoders
- Reinforcement Learning for Generation
- Interactive Generative Systems
- Fashion Generation with Generative Models
- Story Generation with Generative Models
- Character Generation with Generative AI
- Generative Modeling for Simulation
- Data Augmentation Techniques with Generative Models
- Future Directions in Generative AI
A Beginner’s Guide to Generative Design | Generative AI
Introduction
Generative design is a way of creating digital things that explores all the possible outcomes by using computer algorithms and ideas that come from nature. This book is great for people who are just starting to learn about invention and creativity. It offers an interesting look at these topics and explains how they work and what they can be used for.
How does generative design work?
Using computer programs and set parameters, generative design looks at different design options, which are often affected by optimization goals or natural events. It is possible to change how design problems, constraints, and goals are stated by using algorithms.
The workflow typically involves several key steps:
Define Parameters and Constraints: The designer describes the factors that characterize the issue area, such as the qualities of the materials, production restrictions, performance requirements, and other pertinent details.
Generate Design Variations: The program generates many design alternatives, from simple forms to complicated geometries, based on specified factors and limits by using computational methods.
Evaluate Designs: Considerations such as structural integrity, weight optimization, aerodynamics, and aesthetic appeal are weighed against preset goals and restrictions while the design is evaluated through the use of simulations, analysis, or computer methods.
Iterate and Refine: Until acceptable solutions are identified or a predetermined stopping threshold is met, the program iteratively improves designs.
Select Final Design: The designer may evaluate the produced designs when iterations are complete and select the best one based on their tastes, the needs of the project, and other pertinent considerations.
Computation and automation are used in generative design to extend the design space and provide creative solutions that push the frontiers of efficiency and originality in domains such as engineering, product design, and architecture.
What problems does generative design solve?
Generated design quickly creates a lot of creative options, especially when cloud computing is used. Users must weigh tradeoffs in order to find a balance between robust and lightweight options. Rapid innovation businesses use generative design a lot because it speeds up the delivery of new products.
Product differentiation: The use of generative design defies convention by producing innovative, high-performing components and goods that outperform specifications and provide a challenge to rivals.
Expert results (even from novice engineers): Is the skills gap causing you concern? With the use of generative design, even a mechanical engineer with no prior experience may now produce a part.
Optimized product costs: Reducing over designed elements is one way that generative design may reduce costs. Though dependable, these designs could need more resources or intricate manufacture than is necessary.
Optimized reliability: Conduct stress assessments on the generative design outputs to confirm the designs' robustness and quality. This guarantees that your design functions in actuality.(It also saves costs in manufacturing and service support.)
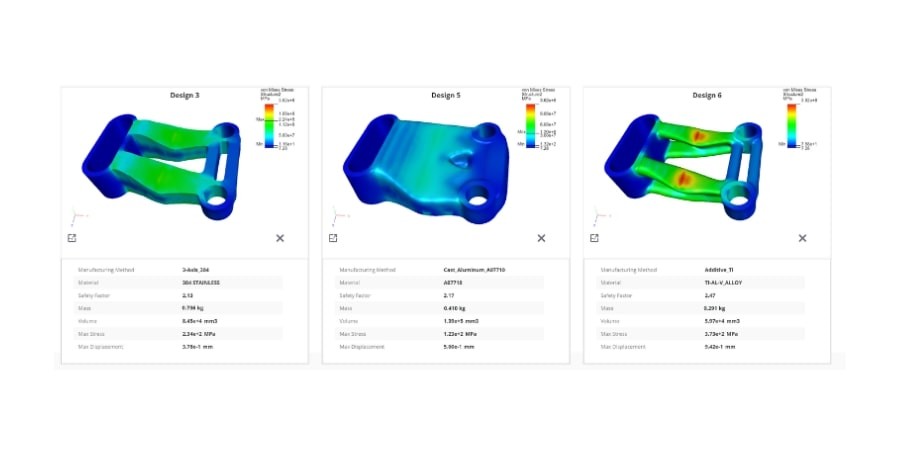
Benefits of generative design
Make impossible designs possible:
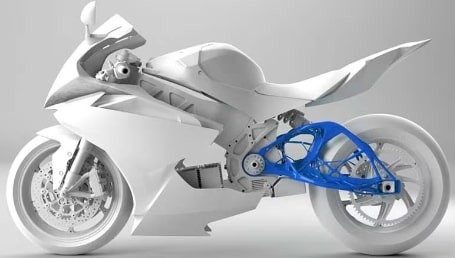
Generative design enables the creation of internal lattices and complicated structures that are optimized. Certain shapes can't be produced using conventional production techniques. Rather, they are constructed by innovative additive manufacturing techniques.
Explore a wider range of design options:
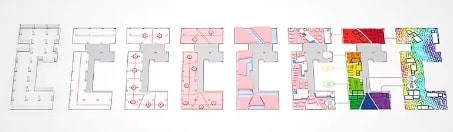
A machine can come up with hundreds of ideas in the time it takes you to come up with one, plus the data that shows which designs work the best.
Optimize for materials and manufacturing methods:

The program will provide high-performing design solutions depending on criteria and goals that you specify. The program settles disagreements between design limitations so you can concentrate on creating.
From aerospace to architecture and construction
The field is utilizing generative design, which has left the lab. Find out how the most creative businesses in the world are now utilizing this technology.
Automotive
Autodesk generative design is being utilized by organizations that are reshaping the automobile industry, from parts consolidation to light weighting components.
Aerospace
Using generative design, the aerospace industry is exploring new design possibilities and enhancing performance, with design and production goals centered around weight reduction, environmental impact, and safety.
Consumer goods
Productivity and creativity are enhanced when several CAD-ready, process-aware solutions to a design challenge may be produced concurrently.
Architecture and construction
Generative design technology may assist you in exploring goals and limitations outside of manufacturing, as seen by the arrangement and style of the Autodesk Toronto headquarters.
Industrial machinery
Producers of specialized tools and machinery are demonstrating how Autodesk generative design can support them in overcoming obstacles to innovation.
Building products
The utilization of additive manufacturing and generative design is enabling providers of industrial construction items to simplify intricate assembly.
Related manufacturing technologies
You can get all the software you need for design for production at Autodesk. Discover some of the other cutting-edge technologies we create.
Internal lattice structures

Design components that are lightweight and have features that are unique to your use case.
Topology optimization
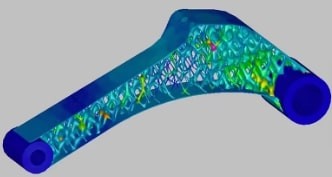
Generate shapes with weight and stiffness optimizations depending on the part's limitations and loads.
Trabecular structures

Assist patients in healing by precisely scaling and dispersing microscopic holes across solid materials to provide surface roughness that resembles bone in medical implants.
Complex part simulation
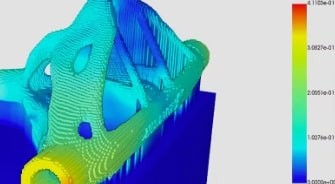
When creating big geometries for additive manufacturing, use thermomechanical modeling techniques.
Going Forward with Generative Design
We hope that has clarified some of your concerns regarding the models that appear unnatural that are produced via generative design. To put it briefly, it's just a new yet effective technology that enables businesses to produce their finest ideas faster.
Conclusion
By utilizing automation and computer algorithms, generative design is transforming the creation of digital art. It gives designers the freedom to push limits, maximize performance, and explore countless alternatives. Taking up generative design means adopting an innovative, exploratory, and iterative attitude that will change the way goods are conceived, built, and produced in all sectors of the economy.
